| trait | R² | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| intelligent | 0.87 | < 0.001 |
| educated | 0.80 | < 0.001 |
| pleasant | 0.79 | < 0.001 |
| self-confident | 0.73 | < 0.001 |
| prestigious | 0.73 | < 0.001 |
| friendly | 0.67 | < 0.001 |
Native and non-native perceptions of Norwegian accents
Kamil Malarski, Magdalena Wrembel, Kamil Kaźmierski, Witosław Awedyk
57th Annual Meeting of the Societas Linguistica Europaea
August 21st, 2024, Helsinki
norwegian-accents-sle2024.netlify.app



Accent and dialect variation in Norway
- High dialectal variation across all linguistic domains i.e. morphosyntax, phonology, lexicon
- Four broad dialect areas, in fact many more, including sociolects (Helleland and Papazian 2005)
- South-Eastern accents seen as the most standard (Johnsen 2015)
- Inclusivity towards dialects
Dialectal areas
- Western Norwegian (Vestnorsk)
- Eastern Norwegian (Østnorsk)
- Trøndelag dialect (Trøndersk)
- Northern Norwegian (Nordnorsk)
Kristoffersen, Gjert. 2000. The phonology of Norwegian. Oxford: OUP.
Why some accents are seen as better or worse than others
- Accents as indexes of how people from the region are seen
- Dependent on salient, easily identifiable linguistic features (Llamas et al. 2016)
- The person “down the street” will always have a stronger accent than the person you are talking to (Preston and Niedzielski 2003)
- Voice parametrics (f0 especially, creaky voice)
- Intelligibility + mergers potentially causing misunderstandings (Labov 2010)
Perceptions of Norwegian accents (1/2)
- Stratified socially (Johnsen 2015)
- Western Oslo accents more prestigious than working-class or multicultural Oslo accents (Aasheim 1995, Johnsen 2015, Svendsen and Røyneland 2008)
- Northern Norwegian accents perceived more negatively than Southern (Sollid 2014)
Perceptions of Norwegian accents (2/2)
- Mixing or switching between dialects seen negatively (Røyneland 2017)
- Non-Oslo dialects viewed as more Norwegian (Røyneland 2017)
- Boys with foreign appearance seen as less Norwegian when using Oslo dialect than when using other dialects (Røyneland 2017: 101)
Previous studies :: methods
- A lot of studies on how upper / West Oslo accents and dialects are perceived, both using the verbal guise technique, as well as surveys in different forms (Dahl 2002; Jensen 2006: 73, Lund 2006, Hult 2008, Kristiansen 1995)
- Nine Norwegian accents tested on a scale from ‘nice’ to ‘ugly’ (Voje 1979)
Previous studies :: findings
- Positive attitudes in Tromsø towards other dialects (Satermo and Sollid 2021)
- Changing one’s dialect seen as incorrect (Satermo and Sollid 2021)
- Negative attitudes by urban Vika speakers towards upper Oslo dialects (Jensen 2006, Lund 2006)
Our Study
Research questions
- Are some accents of Norwegian perceived differently than others?
- Do L2/L3 learners of Norwegian attribute similar aesthetic judgments to Norwegian speech as Norwegian listeners do?
- Are there any acoustic correlates of these judgments (e.g. high-pitched voice, female/male voice, the presence of uvular [ʁ]) ?
Design
- Online survey in Qualtrics
- Reading passage in Norwegian (Nordavinden og sola from the Norwegian dialects database www.hf.ntnu.no/nos)
- Selected speech samples \(N=14\)
- 10 middle-aged native Norwegians (5 f, 5 m) from five dialect areas: the Tromsø area, Trondheim, Stavanger, Kristiansand, and Oslo
- 4 controls: non-native accents of Norwegian of different strength (L1 Polish)
- 10 middle-aged native Norwegians (5 f, 5 m) from five dialect areas: the Tromsø area, Trondheim, Stavanger, Kristiansand, and Oslo
Our data (L1 NO)
Our data (L3 NO)
Procedure
7-point Likert scale:
- Education level
- Pleasantness
- Intelligence
- Prestige
- Friendliness
- Self-confidence
- Distance / proximity
Open questions:
- Likes / dislikes
- Characteristic features
- Region of origin of speaker
Samples presented in randomized order
Duration: ca. 20 mins
Participants :: 3 groups
- Polish instructed learners of Norwegian living in Poland \(n = 47\)
- Polish naturalistic learners of Norwegian residing in Norway \(n = 25\)
- Norwegian native speakers as controls \(n = 45\)
Participants :: profiles
- Gender (72 f, 39 m, 2 non-binary, 2 undisclosed), Age (mean = 33.5)
- Residence in Norway (present or past)
- Length of learning Norwegian
- Language use frequency
- Proficiency level in Norwegian, English, Polish
Analyses
- Likert scale ratings
- Joint group analysis
- Across-group comparison
- Across-accent comparison
- Attitudes to individual accents (likes/dislikes)
- Accent identification
- Characgeristic features of accents (qualitative)
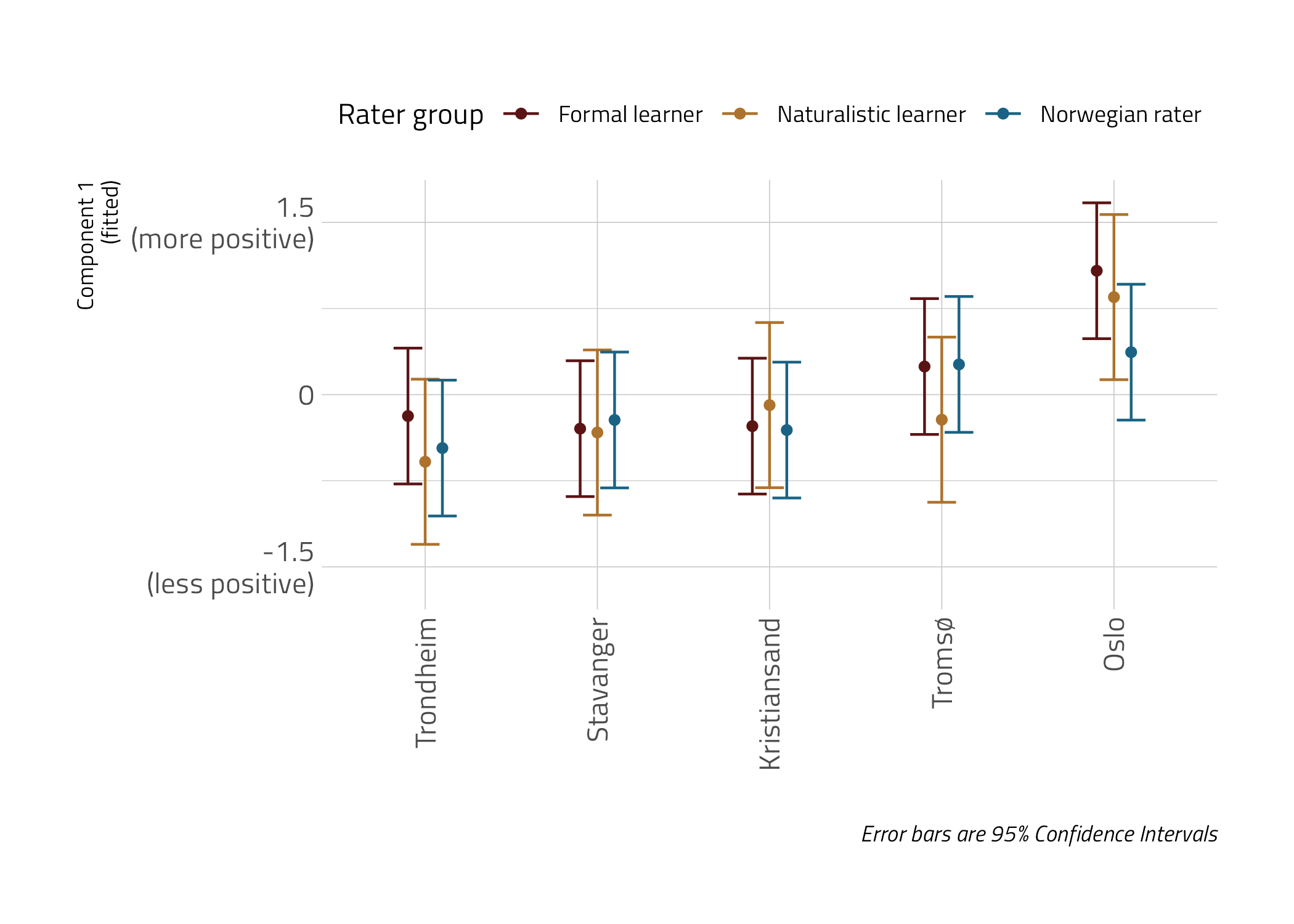
PCA :: Component 1
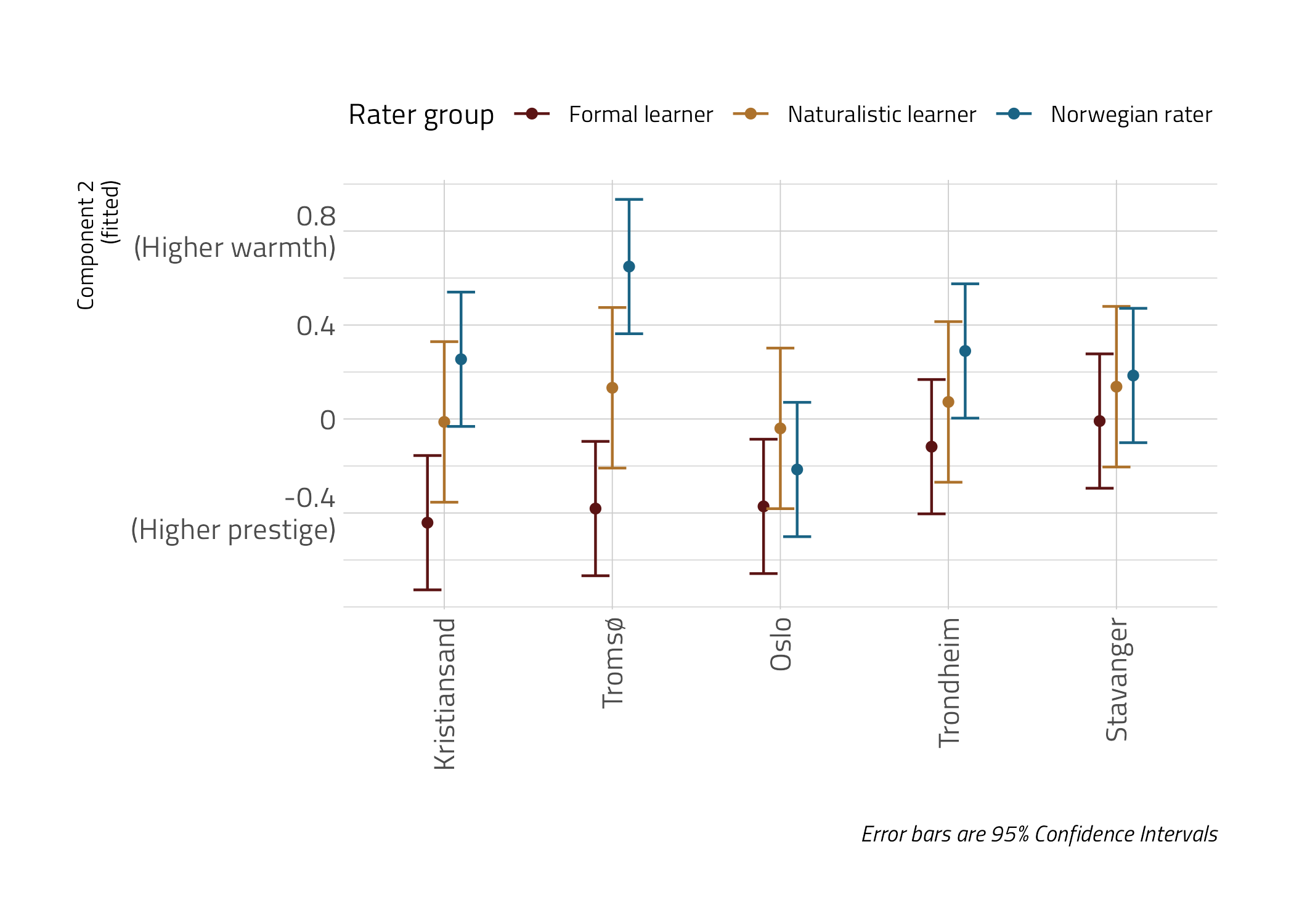
PCA :: Component 2
| trait | R² | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| friendly | 0.63 | < 0.001 |
| pleasant | 0.40 | < 0.001 |
| intelligent | -0.12 | < 0.001 |
| educated | -0.37 | < 0.001 |
| prestigious | -0.47 | < 0.001 |
Open answers (identification)
- Few learners were guessing correctly the origin of the accent
- Not all native speakers were able to guess the locations
- Over 100 responses per voice
- Mandal :: (corr) : Mandal (2), Kristiansand (8), Flekkefjord (2), Vest-Agder (7), Sørlandet (22), (incorr) : Bergen (6), Stavanger (5)
- Kristiansand :: (corr) : Kristiansand (11), southern Norway (18), Vest-Agder (7), (incorr): Bergen (6), Stavanger (5), Trondheim (8), Hamar (2), Lindesnes (1), Hordaland (1), Førde (1)
Open answers (attitudes)
- In all cases, comments were :: positive > neutral > negative
- Over 100 comments for each accent
- Many listeners commented on uvular [ʁ] sounds when they occurred (Kristiansand, Mandal, Stavanger)
- Other features noticed: prosody, ka - hva replacement
- In general, comments on likes, dislikes, “flow”, “melody”, softness and friendliness
Conclusions
- Different accents in Norway are given different aesthetic and social attributions
- Oslo viewed most positively
- Perceptions are aligned along different criteria (Components), e.g. Tromsø friendly but not prestigious, Oslo prestigious but not that warm or pleasant
- In Component 2 (warmth vs. prestige), 3 groups of respondents differed in their responses; learners rated all accents more prestigious but less friendly / warm
- With more exposure and social context, non-native speakers seem to be more inclusive towards accentual variation
Next steps
- Sociolinguistics vs. Language acquisition perspective
- f0 correlates ~ perception scores
- Potentially stigmatised features (e.g. tjukk l [ɽ], word-final palatalisation of /n/) + deviation from standard ~ perception scores
- Suggestions?
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Jørn Almberg for access to the speech sample database and to Jacques Koreman for consultations.
The research leading to these results has received funding from Norway Grants - the Norwegian Financial Mechanism 2014-2021 project number 2019/34/H/HS2/00495.
